link to page 2 link to page 2 link to page 2 link to page 2 link to page 3 link to page 4 link to page 9 link to page 23 link to page 23 link to page 30 link to page 38 link to page 45 link to page 46 link to page 46 link to page 23 link to page 23
link to page 3 link to page 3

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
A person meets the age requirements if the person was aged under 65 when the access
request in relation to the person was made.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows:
• the applicant was aged under 65 when their access request was received as valid (that is,
complete)
Applicants that meet the age
Go to
Section 5.1 Does the applicant meet the
requirements
residence requirements?
Applicants that do not meet the age
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
requirements
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
▪
5. Access – Residence Requirements
5.1 Does the applicant meet the residence requirements?
Legislation
Section 23 Residence requirements
(1) A person meets the residence requirements if the person:
(a) resides in Australia; and
(b) is one of the following:
(i) an Australian citizen;
(ii) the holder of a permanent visa;
(iii) a special category visa holder who is a protected SCV holder.
(2) In deciding whether or not a person resides in Australia, regard must be had to:
(a) the nature of the accommodation used by the person in Australia; and
(b) the nature and extent of the family relationships the person has in Australia; and
(c) the nature and extent of the person’s employment, business or financial ties with
Australia; and
(d) the nature and extent of the person’s assets located in Australia; and
(e) the frequency and duration of the person’s travel outside Australia; and
(f) any other matter relevant to determining whether the person intends to remain
permanently in Australia.
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 3 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 3 of 52
link to page 4 link to page 4 link to page 4

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the applicant:
• lives in Australia for most of the year; and
• is an Australian Citizen; or
• is the holder of a permanent visa; or
• is the holder of a protected Special Category Visa (SCV)
Applicants that meet the residency
Go to
Section 6.1 - List A
requirements
Applicants that do not meet the Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
residency requirements
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
6.Access – Streamlined Decisions
6.1 List A
List A conditions that are likely to meet the disability requirements.
•
Note: A person does not need to have a condition on List A to become a participant of the
NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Do you meet the disability requirements?
Applicants that have a condition on
Are likely to meet the disability requirements.
List A
Go to
Section 6.2 0-25 Hearing Impairments to
assess if the applicant also meets early intervention.
Applicants that do not have a
Go to
Section 6.2 0-25 Hearing Impairments
condition on List A
6.2 0-25 Hearing Impairments
An applicant meets the early intervention requirements without further assessment if they:
• are aged between birth and 25 years of age; and
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 4 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 4 of 52
link to page 30

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• have confirmed results from a specialist audiological assessment (including
electrophysiological testing when required) consistent with auditory neuropathy or hearing
loss ≥ 25 decibels in either ear at 2 or more adjacent frequencies, which is likely to be
permanent.
What to consider
This streamlined access approach for early intervention acknowledges a rich body of evidence
that recognises that early intervention supports up to and including the age of 25 is critical for
people with hearing impairment as the developing brain requires consistent and quality sound
input and other support over that period to develop normally and ameliorate the risk of lifelong
disability.
This same body of evidence suggests that brain development and language capability have
been achieved by the age of 26. Therefore, adults aged 26 years and over are not immediately
accepted to be likely to benefit from the same early intervention approach because there is no
requirement to support the development of the auditory pathways. Adults aged 26 years and
over with hearing impairment will therefore be assessed normally, on a case-by-case basis,
having regard to the availability of all relevant evidence.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - What about people aged between 0 and 25
with a hearing impairment?
Applicants that have a List A condition who are under 7
Applicants that meet the hearing
Meets the Disability (List A) and Early Intervention
impairment criteria
Requirements
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
Applicants that don’t meet the
Go to
6.3 List D
hearing impairment criteria
Applicants that have a List A condition who are over 7
Applicants that meet the hearing
Meets the Disability (List A) and Early Intervention
impairment criteria
Requirements
Go to the knowledge articles Prepare to make an
access decision and Submit an access decision
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 5 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 5 of 52
link to page 9 link to page 8 link to page 8 link to page 8 link to page 6 link to page 15 link to page 6

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that don’t meet the
Go to
Section 7 Early Intervention Requirements
hearing impairment criteria
Applicants that DON’T have a List A condition who are over 7
Applicants that meet the hearing
Meets the Early Intervention Requirements
impairment criteria
Go to
Section 6.5 List B
Applicants that don’t meet the
Go to
Section 6.5 List B
hearing impairment criteria
Applicants that DON’T have a List A condition who are under 7
Applicants that meet the hearing
Meets the Early Intervention Requirements
impairment criteria
Go to
Section 6.5 List B
Applicants that don’t meet the
Go to
Section 6.3 List D
hearing impairment criteria
6.3 List D
Where a child under the age of 7 has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they will meet
the early intervention requirements without further assessment.
•
Note: A child does not need to have a List D condition to become a participant of the NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Do you need early intervention?
For applicants under the age of 7
Applicants that have a condition on
Meet the early intervention requirements.
List D
Go to
Section 8. Access Disability Requirements
Applicants that do not have a
Go to
Section 6.4 Developmental Delay
condition on List D
6.4 Developmental Delay
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(1)
A person
meets the early intervention requirements if:
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 6 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 6 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(a)
the person:
(iii)
is a child who has developmental delay; and
(b)
the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is likely
to benefit the person by reducing the person’s future needs for supports in relation to disability;
and
(c)
the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is likely
to benefit the person by:
(i)
mitigating or alleviating the impact of the person’s impairment upon the functional
capacity of the person to undertake communication, social interaction, learning, mobility,
selfcare or self-management; or
(ii)
preventing the deterioration of such functional capacity; or
(iii)
improving such functional capacity; or
(iv)
strengthening the sustainability of informal supports available to the person, including
through building the capacity of the person’s carer.; and
(d)
the CEO is satisfied any early intervention supports that would be likely to benefit the
person as mentioned in paragraphs (b) and (c) would be NDIS supports for the person.
Section 9 Definitions
Developmental delay means a delay in the development of a child under 6 years of age that:
(a) is attributable to a mental or physical impairment or a combination of mental and physical
impairments; and
(b) results in substantial reduction in functional capacity in one or more of the following areas
of major life activity:
(i) self-care;
(ii) receptive and expressive language;
(iii) cognitive development;
(iv) motor development; and
(c) results in the need for a combination and sequence of special interdisciplinary or generic
care, treatment or other services that are of extended duration and are individually planned
and coordinated.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the child is younger than 6 on
the day we determine they have developmental delay.
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 7 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 7 of 52
link to page 8 link to page 8 link to page 10 link to page 18 link to page 23 link to page 15 link to page 15 link to page 10

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - What about children younger than 6 with
developmental delay?
Applicants that meet the
Meet the early intervention requirements.
Developmental Delay criteria
Go to
Section 6.5 - List B
Applicants that do not meet the
Go to
Section 6.5 - List B
Developmental Delay criteria
6.5 List B
Where an applicant has been diagnosed with a condition on List B, they will be considered to
have a disability attributable to one or more conditions that are likely to result in a permanent
impairment.
For applicants diagnosed with a condition on List B, you will only need to assess whether the
applicant:
• has substantially reduced functional capacity to perform one or more activities;
• is affected in their capacity for social or economic participation; and
• is likely to require support under the NDIS for their lifetime.
•
Note: A person does not need to have a condition on List B to become a participant in the
NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Is your impairment likely to be permanent?
For applicants who meet the 0-25 Hearing Loss, List D or Developmental Delay criteria
Applicants that have a condition
Go to
Section 8.3 Doe
s the applicant meet 24(1)c?
on List B
Applicants that do not have a
Go to
Section 8 Disabil
ity Access – Disability
condition on List B
Requirements
For applicants who DON’T meet the 0-25 Hearing Loss, List D or Developmental Delay
criteria
Applicants that have a condition
Go to Section
7.2 Does the applicant meet 25(1)b
on List B
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 8 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 8 of 52
link to page 9 link to page 23 link to page 2 link to page 15 link to page 15 link to page 3

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that do not have a
Go to Section
7 Early Intervention requirements
condition on List B
7 Access - Early Intervention Requirements
For children under the age of 7 they are first assessed against the
early intervention criteria. If
they do not meet, then assess them against the
disability requirements.
Before you commence the assessment, you must ensure the applicant meets both the
age
requirements and
residency requirements.
7.1 Does the applicant meet Section 25(1)(a)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(1) A person meets the early intervention requirements if:
(a) the person:
(i) has one or more identified intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory or
physical impairments that are, or are likely to be, permanent; or
(ii) has one or more identified impairments to which a psychosocial disability is
attributable and that are, or are likely to be, permanent
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows:
• the applicant has an impairment (a loss or significant change in their body’s functions or
structure, or how they think and learn); and
• the impairment is intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory, or physical in nature; and
• the impairment is, or is likely to be, permanent.
•
Note: When an applicant is diagnosed with a condition on List B or List D, they meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant has completed all available and
appropriate treatment options, and that there are no recommended treatment options likely
to remedy the impairment?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 9 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 9 of 52
link to page 23 link to page 23 link to page 15 link to page 15

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• Does the evidence contain recommendations for treatments which have not been
demonstrated to have been explored?
• Does the evidence indicate that the applicant requires further treatment, and that this
treatment has some prospect of success?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant requires ongoing treatment, but that it is
for maintenance purposes only?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the impairment is degenerative in nature, and that
treatment will not improve the impairment?
In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• What treatments have been undertaken and what were the outcomes?
• If there are evidence-based treatments not undertaken, why were they considered and
deemed not suitable?
• What further/ongoing treatments have been recommended and what are the expected
outcomes of these treatments?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Do you need early intervention?
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 7.2 - Does the applicant meet Section
25(1)(a)
25(1)(b)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for early intervention.
25(1)(a)
You will now assess them against the disability
requirements.
Go to
Section 8.1 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(a)?
Note: If the applicant has a List A Disability you can
proceed to knowledge articles Prepare to make an
access decision and Submit an access decision
7.2 Does the applicant meet Section 25(1)(b)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 10 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 10 of 52
link to page 12 link to page 12

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(1) A person meets the early intervention requirements if:
(b) the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is
likely to benefit the person by reducing the person’s future needs for supports in
relation to disability
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows that early intervention
supports for the applicant’s permanent impairment/s will reduce their need for disability-related
supports in the future.
•
Note: If an applicant has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they meet this criterion
without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and indicate
that this intervention will mean the applicant needs less disability supports in the future?
• Does the evidence note which specific supports the applicant will no longer require should
early intervention be undertaken?
• Does the evidence indicate that early intervention is likely to result in greater independence
for the applicant?
• If the applicant has accessed intervention before, is the outcome noted? Did previous
intervention reduce their need for disability related supports?
• Is the recommended support of a functional nature, or capacity building in nature?
• In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• How the applicant's impairment is likely to impact them over time?
• What supports the applicant will require if they don’t receive intervention?
• What supports the applicant currently requires, and what supports (if any) the applicant is
likely to require after intervention?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - How will early intervention help you?
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 7.3 - Does the applicant meet Section
25(1)(b)
25(1)(c)?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 11 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 11 of 52
link to page 15 link to page 15

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for early intervention.
25(1)(b)
You will now assess them against the disability
requirements.
Go to
Section 8.1 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(a)?
Note: If the applicant has a List A Disability you can
proceed to knowledge articles Prepare to make an
access decision and Submit an access decision
7.3 Does the applicant meet Section 25(1)(c)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(1) A person meets the early intervention requirements if:
(c) the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is
likely to benefit the person by:
(i) mitigating or alleviating the impact of the person’s impairment upon the functional
capacity of the person to undertake communication, social interaction, learning,
mobility, self‑care or self‑management; or
(ii) preventing the deterioration of such functional capacity; or
(iii) improving such functional capacity; or
(iv) strengthening the sustainability of informal supports available to the person,
including through building the capacity of the person’s carer.
When is this criterion considered met?
• This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows early intervention supports
will help the applicant by:
• addressing the impact of their impairment on their ability to move around, communicate,
socialise, learning, look after themselves, or organise their life
• preventing their functional capacity from getting worse
• improving their functional capacity
• supporting their informal supports to build their skills to help the applicant.
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 12 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 12 of 52
link to page 14 link to page 14 link to page 15 link to page 15

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
•
Note: If an applicant has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they meet this criterion
without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and detail how
this intervention will mitigate or alleviate the impact of the applicant's permanent
impairment on their functional capacity?
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and detail how
this intervention will prevent the applicant's functional capacity from declining?
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and detail how
this intervention will improve the applicant's functional capacity?
• Does the evidence indicate that intervention is likely to strengthen the sustainability of
informal supports available to the person, and result in a decreased need for formal
disability related supports?
• In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• How the applicant's impairment is likely to impact them over time?
• What supports the applicant will require if they don’t receive intervention?
• What supports the applicant currently requires, and what supports (if any) the applicant is
likely to require after intervention?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - How will early intervention help you?
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 7.4 - Does the applicant meet Section
25(1)(c)
25 (1)(d)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for early intervention.
25(1)(c)
You will now assess them against the disability
requirements.
Go to
Section 8.1 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(a)?
Note: If the applicant has a List A Disability you can
proceed to knowledge articles Prepare to make an
access decision and Submit an access decision
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 13 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 13 of 52
link to page 15 link to page 15 link to page 15 link to page 15

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
7.4 Does the applicant meet section 25(1)(d)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(d) … any early intervention supports that would be likely to benefit the person as
mentioned in paragraphs (b) and (c) would be NDIS supports for the person.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows that early intervention
supports required are NDIS supports.
•
Note: If an applicant has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they meet this criterion
without further assessment.
What to consider
Whether or not funding is available through other general systems is not the test of whether it
is most appropriately funded or provided through the NDIS. For example, the fact that the
health system does not adequately fund what is essentially clinical treatment (or some other
form of support that is more appropriately funded through the health system) does not make it
the responsibility of the NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Is your early intervention most appropriately
funded by the NDIS?
For applicants who do not have a List A impairment
Applicants that meet Section
Meet the early intervention requirements.
25(1)(d)
Make note of this, as you will now assess them
against the disability requirements.
Go to
Section 8.1 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(a)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for early intervention.
25(1)(d)
You will now assess them against the disability
requirements.
Go to
Section 8.1 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(a)?
For applicants who have a List A impairment
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 14 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 14 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that meet Section
Meet the disability and early intervention
25(1)(d)
requirements.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for early intervention,
however do
25(1)(d)
satisfy the disability requirements.
Please follow the process in knowledge
articlesPrepare to make an access decision and
Submit an access decision.
8 Access – Disability Requirements
8.1 Does the applicant meet Section 24(1)(a)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(a) the person has a disability that is attributable to one or more intellectual, cognitive,
neurological, sensory or physical impairments or the person has one or more
impairments to which a psychosocial disability is attributable.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows:
• the applicant has a disability (a reduction or loss in their ability to do things); and
• their disability is caused by an impairment (a loss or significant change in their body’s
functions or structure, or how they think and learn); and
• the impairment is intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory, or physical in nature.
•
Note: Where an applicant has been diagnosed with a List A or List B condition, they will
meet this criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate both that the applicant has an impairment, and that the
impairment is resulting in a disability?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 15 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 15 of 52
link to page 16 link to page 16 link to page 16 link to page 16

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant is reduced in their ability to do things,
however this reduction cannot be reasonably attributed to an impairment?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant has a loss or significant change in one of
their body's functions or structure, or in how they think and learn; however, there is no
indication that this is causing a reduction or loss in their ability to do things?
•
Note: A diagnosis is not required to meet this criterion: if the evidence shows the person
has a disability caused by a relevant impairment, then they will meet 24(1)(a) – this is
because we assess based on the impairment/functional impact.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Is your disability caused by an impairment?
If the person does NOT meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.2 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(a)
24(1)(b)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
24(1)(a)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision.
If the person does meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.2 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(a)
24(1)(b)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability,
however do satisfy the
24(1)(a)
early intervention requirements.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
8.2 Does the applicant meet Section 24(1)(b)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 16 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 16 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(b) The impairment or impairments are, or are likely to be, permanent
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the applicant has a:
• permanent impairment; or
• likely permanent impairment.
•
Note: Where an applicant has been diagnosed with a List A or List B condition, they will
meet this criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant has completed all available and
appropriate treatment options, and that there are no recommended treatment options likely
to remedy the impairment?
• Does the evidence contain recommendations for treatments which have not been
demonstrated to have been explored?
• Does the evidence indicate that the applicant requires further treatment, and that this
treatment has some prospect of success?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant requires ongoing treatment, but that it is
for maintenance purposes only?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the impairment is degenerative in nature, and that
treatment will not improve the impairment?
In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• What treatments have been undertaken and what were the outcomes?
• If there are evidence-based treatments not undertaken, why were they considered and
deemed unsuitable?
• What further/ongoing treatments have been recommended and what are the expected
outcomes of these treatments?
For further information, refer to Is your impairment likely to be permanent? | NDIS
If the person does NOT meet the Early Intervention criteria
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 17 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 17 of 52
link to page 18 link to page 18 link to page 18 link to page 18

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.3 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(b)
24(1)(c)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
24(1)(b)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
If the person does meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.3 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(b)
24(1)(c)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability,
however do satisfy the
24(1)(b)
early intervention requirements.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
8.3 Does the applicant meet Section 24(1)(c)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(c) The impairment or impairments result in substantially reduced functional capacity to
undertake one or more of the following activities: The impairment or impairments
result in substantially reduced functional capacity to undertake one or more of the
following activities:
(i) communication;
(ii) social interaction;
(iii) learning
(iv) mobility
(v) self-care
(vi) self-management
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 18 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 18 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
…
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the permanent impairment, or
permanent impairments combined, results in substantially reduced functional capacity in one
or more of the following activities:
• Communication: how they speak, write or use sign language and gestures.
• Social interaction: how they make and keep friends, interact with the community, and cope
with feelings and emotions in social situations.
• Learning
: how they learn, understand and remember new things, and practise and use new
skills.
• Mobility: how they move around home and the community and how they get in and out of
bed or a chair.
• Self-care: how they partake in personal care, hygiene, grooming, eating and drinking, and
health.
• Self-management (if older than 6): how they organise their life, make decision, solve
problems and manage money.
•
Note: When an applicant has been diagnosed with a List A condition, they will meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant is unable to participate effectively or
completely (i.e., across the whole or majority of tasks) in one or more activities, without
formally prescribed equipment?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant is unable to participant effectively or
completely in one or more activities, and usually requires the assistance of another
person?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant would be unsafe to complete one or
more tasks required to participate in an activity without formally prescribed equipment or
assistance from another person?
• Does the evidence indicate that the applicant is able to participate in each activity
effectively by using commonly used items?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 19 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 19 of 52
link to page 20 link to page 20 link to page 20 link to page 20

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• Does the evidence indicate that the applicant is able to participate in each activity
effectively, albeit more slowly or in a different way?
• Would completing tasks more slowly or in a modified way, or using commonly used items,
relieve the applicant's need for personal assistance?
In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• What specific tasks the applicant cannot complete without support?
• Why the applicant requires support?
• How often the applicant requires support, and what that support looks like?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Does your impairment substantially reduce
your functional capacity?
If the person does NOT meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.4 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(c)
24(1)(d)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability support from the NDIS.
24(1)(c)
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
If the person does meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.4 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(c)
24(1)(d)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability,
however do satisfy the
24(1)(c)
early intervention requirements.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
8.4 Does the applicant meet Section 24(1)(d)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 20 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 20 of 52
link to page 21 link to page 21 link to page 21 link to page 21

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(d) The impairment or impairments affect the person’s capacity for social or economic
participation.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the permanent impairment, or
permanent impairments combined, affects the applicant’s social or economic participation.
•
Note: Where an applicant has been diagnosed with a List A condition, they will meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant's social participation (e.g., their capacity
to play sport, go to the movies, see friends, etc.) is affected by their permanent
impairment/s - in any way?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant's economic participation (e.g., their
capacity to travel, to find or maintain voluntary or paid work, etc.) is affected by their
permanent impairment - in any way?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant's social and economic participation is not
impacted in any way, and that they can fully engage without any assistance?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Does your impairment affect your social, work
or study life?
If the person does NOT meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.5 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(d)
24(1)(e)?
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability support from the NDIS.
24(1)(d)
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
If the person does meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Go to
Section 8.5 - Does the applicant meet Section
24(1)(d)
24(1)(e)?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 21 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 21 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability,
however do satisfy the
24(1)(d)
early intervention requirements.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
8.5 Does the applicant meet Section 24(1)(e)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(e) The person is likely to require NDIS supports under the National Disability Insurance
Scheme for the person’s lifetime.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the applicant:
• will require NDIS supports under the National Disability Insurance Schemes s their
lifetime; or
• is likely to require the support of the NDIS for their lifetime.
•
Note: Where an applicant has been diagnosed with a List A condition, they will meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant is likely to require disability supports that
are not clinical in nature, and that focus on their functional ability, for their lifetime?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the applicant will likely be substantially reduced in
their functional capacity (in a relevant activity) for their lifetime, despite any interventions?
• Are there any recommendations for interventions that are likely to improve the applicant's
functional capacity, and reduce their future need for disability related supports?
• If the applicant is a child or young adult, does the evidence indicate that significant
functional improvements can be expected - either as they develop, or through
interventions?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 22 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 22 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• Does the applicant's need for support relate to a health condition, and is that support more
appropriately funded by the health system?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Does your impairment affect your social, work
or study life?
If the person does NOT meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Meet the disability requirements.
24(1)(e)
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability support from the NDIS.
24(1)(e)
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
If the person does meet the Early Intervention criteria
Applicants that meet Section
Eligible for both Disability and Early Intervention.
24(1)(e)
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
Applicants that do not meet Section
Are not eligible for disability,
however do satisfy the
24(1)(e)
early intervention requirements.
Please follow the process in knowledge articles
Prepare to make an access decision and Submit an
access decision
9 ER – Residence Requirements
9.1 Does the participant continue to meet the residence requirements?
Legislation
Section 23 Residence requirements
(1) A person meets the residence requirements if the person:
(a) resides in Australia; and
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 23 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 23 of 52
link to page 24

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(b) is one of the following:
(i) an Australian citizen;
(ii) the holder of a permanent visa;
(iii) a special category visa holder who is a protected SCV holder.
(2) In deciding whether or not a person resides in Australia, regard must be had to:
(a) the nature of the accommodation used by the person in Australia; and
(b) the nature and extent of the family relationships the person has in Australia; and
(c) the nature and extent of the person’s employment, business or financial ties with
Australia; and
(d) the nature and extent of the person’s assets located in Australia; and
(e) the frequency and duration of the person’s travel outside Australia; and
(f) any other matter relevant to determining whether the person intends to remain
permanently in Australia.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the participant:
• lives in Australia for most of the year; and
• is an Australian Citizen; or
• is the holder of a permanent visa; or
• is the holder of a protected Special Category Visa (SCV)
Participants that continue to meet
Go to
Section 10.1 - List A
the residence requirements
Participants that no longer meet the
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
residence requirements
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check, or
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
10 ER – Streamlined Decisions
10.1 List A
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 24 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 24 of 52
link to page 30 link to page 25

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
List A conditions that are likely to meet the disability requirements.
•
Note: A person does not need to have a condition on List A to become a participant of the
NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Do you meet the disability requirements?
For applicants under the age of 7
Applicants that have a condition on
Meet the disability requirements.
List A
Please follow the process in either :
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Applicants that do not have a
Go to
Section 10.3 - List D
condition on List A
Applicants aged 7 and over
Applicants that have a condition on
Meet the disability requirements.
List A
Please follow the process in either :
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Applicants that do not have a
Go to
Section 10.2 - List B
condition on List A
10.2 List D
Where a child under the age of 7 has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they will meet
the early intervention requirements without further assessment.
•
Note: A child does not need to have a List D condition to become a participant of the NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Do you need early intervention?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 25 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 25 of 52
link to page 26

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that have a condition on
Meet the early intervention requirements.
List D
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Applicants that do not have a
Go to Section 10.4
0-25 Hearing Impairments
condition on List D
10.3 0-25 Hearing Impairments
An applicant meets the early intervention requirements without further assessment if they:
• are aged between birth and 25 years of age; and
• have confirmed results from a specialist audiological assessment (including
electrophysiological testing when required) consistent with auditory neuropathy or hearing
loss ≥ 25 decibels in either ear at 2 or more adjacent frequencies, which is likely to be
permanent.
What to consider
This streamlined access approach for early intervention acknowledges a rich body of evidence
that recognises that early intervention supports up to and including the age of 25 is critical for
people with hearing impairment as the developing brain requires consistent and quality sound
input and other support over that period to develop normally and ameliorate the risk of lifelong
disability.
This same body of evidence suggests that brain development and language capability have
been achieved by the age of 26. Therefore, adults aged 26 years and over are not immediately
accepted to be likely to benefit from the same early intervention approach because there is no
requirement to support the development of the auditory pathways. Adults aged 26 years and
over with hearing impairment will therefore be assessed normally, on a case-by-case basis,
having regard to the availability of all relevant evidence.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - What about people aged between 0 and 25
with a hearing impairment?
Applicants who are under the age of 7
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 26 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 26 of 52
link to page 27 link to page 38 link to page 38

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that meet the hearing
Meet the early intervention requirements.
impairment criteria
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Applicants that do not meet the
Go to
Section 10.5 Developmental Delay
hearing impairment criteria
Applicants who are over the age of 7
Applicants that meet the hearing
Meet the early intervention requirements.
impairment criteria
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Applicants that do not meet the
Go to
Section 12 – ER Early Intervention
hearing impairment criteria
requirements
10.4 Developmental Delay
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(1)
A person
meets the early intervention requirements if:
(a)
the person:
(iii)
is a child who has developmental delay; and
(b)
the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is likely
to benefit the person by reducing the person’s future needs for supports in relation to disability;
and
(c)
the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is likely
to benefit the person by:
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 27 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 27 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(i)
mitigating or alleviating the impact of the person’s impairment upon the functional
capacity of the person to undertake communication, social interaction, learning, mobility,
selfcare or self-management; or
(ii)
preventing the deterioration of such functional capacity; or
(iii)
improving such functional capacity; or
(iv)
strengthening the sustainability of informal supports available to the person, including
through building the capacity of the person’s carer.; and
(d)
the CEO is satisfied any early intervention supports that would be likely to benefit the
person as mentioned in paragraphs (b) and (c) would be NDIS supports for the person.
Section 9 Definitions
Developmental delay means a delay in the development of a child under 6 years of age that:
(d) is attributable to a mental or physical impairment or a combination of mental and physical
impairments; and
(e) results in substantial reduction in functional capacity in one or more of the following areas
of major life activity:
(i) self-care;
(ii) receptive and expressive language;
(iii) cognitive development;
(iv) motor development; and
(f) results in the need for a combination and sequence of special interdisciplinary or generic
care, treatment or other services that are of extended duration and are individually planned
and coordinated.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the child is younger than 6 on
the day we determine they have developmental delay.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - What about children younger than 6 with
developmental delay?
Applicants that meet the
Meet the early intervention requirements.
Developmental Delay criteria
Please follow the process in either:
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 28 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 28 of 52
link to page 29 link to page 40 link to page 40 link to page 38 link to page 38 link to page 33 link to page 33

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Applicants that do not meet the
Go to
Section 10.3 - List B
Developmental Delay criteria
10.5 List B
Where an applicant has been diagnosed with a condition on List B, they will be considered to
have a disability attributable to one or more conditions that are likely to result in a permanent
impairment.
For applicants diagnosed with a condition on List B, you will only need to assess whether the
applicant:
• has substantially reduced functional capacity to perform one or more activities;
• is affected in their capacity for social or economic participation; and
• is likely to require support under the NDIS for their lifetime.
•
Note: A person does not need to have a condition on List B to become a participant in the
NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Is your impairment likely to be permanent?
For participants who are under the age of 7
Applicants that have a condition
Go to
Section 12.2 Does the participant meet Section
on List B
25(1)b?
Applicants that do not have a
Go to
Section 12.1 Does the participant meet Section
condition on List B
25(1)a?
For participants who are over the age of 7
Applicants that have a condition
Go to Section 11.3
Does the participant meet Section
on List B
24(1)(c)?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 29 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 29 of 52
link to page 30 link to page 30

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Applicants that do not have a
Go to
Section 11.1 Does the participant meet Section
condition on List B
24(1)a?
11 ER - Disability Requirements
11.1 Does the participant meet Section 24(1)(a)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(a) the person has a disability that is attributable to one or more intellectual, cognitive,
neurological, sensory or physical impairments or the person has one or more
impairments to which a psychosocial disability is attributable
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows:
• the participant has a disability (a reduction or loss in their ability to do things); and
• their disability is caused by an impairment (a loss or significant change in their body’s
functions or structure, or how they think and learn); and
• the impairment is intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory, or physical in nature.
•
Note: Where a participant has been diagnosed with a List A or List B condition, they will
meet this criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate both that the participant has an impairment, and that the
impairment is resulting in a disability?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant is reduced in their ability to do things,
however this reduction cannot be reasonably attributed to an impairment?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant has a loss or significant change in one
of their body's functions or structure, or in how they think and learn; however, there is no
indication that this is causing a reduction or loss in their ability to do things?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 30 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 30 of 52
link to page 31 link to page 31 link to page 31 link to page 31 link to page 26

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
•
Note: A diagnosis is not required to meet this criterion: if the evidence shows the person
has a disability caused by a relevant impairment, then they will meet 24(1)(a) – this is
because we assess based on the impairment/functional impact.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Is your disability caused by an impairment?
For participants under the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.2 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(a)
Section 24(1)(b)?
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 24(1)(a)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
For participants over the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.2 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(a)
Section 24(1)(b)?
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 10.4 0-25 Hearing Impairments
Section 24(1)(a)
11.2 Does the participant meet Section 24(1)(b)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(2) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(b) The impairment or impairments are, or are likely to be, permanent
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the participant has a:
• permanent impairment; or
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 31 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 31 of 52
link to page 33 link to page 33

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• likely permanent impairment.
•
Note: Where a participant has been diagnosed with a List A or List B condition, they will
meet this criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant has completed all available and
appropriate treatment options, and that there are no recommended treatment options likely
to remedy the impairment?
• Does the evidence contain recommendations for treatments which have not been
demonstrated to have been explored?
• Does the evidence indicate that the participant requires further treatment, and that this
treatment has some prospect of success?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant requires ongoing treatment, but that it
is for maintenance purposes only?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the impairment is degenerative in nature, and that
treatment will not improve the impairment?
In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• What treatments have been undertaken and what were the outcomes?
• If there are evidence-based treatments not undertaken, why were they considered and
deemed unsuitable?
• What further/ongoing treatments have been recommended and what are the expected
outcomes of these treatments?
For further information, refer to Is your impairment likely to be permanent? | NDIS
For participants under the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.3 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(b)
Section 24(1)(c)?
Participants that do not meet
Are
not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 24(1)(b)
support from the NDIS.
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 32 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 32 of 52
link to page 33 link to page 33 link to page 26

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
If they do not meet this criterion, they automatically
do not meet Section 25(1)(a).
Please follow the process in:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check, or
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
For participants over the age of 7
For participants over the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.3 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(b)
Section 24(1)(c)?
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 10.4 0-25 Hearing Impairments
Section 24(1)(b)
11.3 Does the participant meet Section 24(1)(c)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(2) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(c) The impairment or impairments result in substantially reduced functional capacity to
undertake one or more of the following activities: The impairment or impairments
result in substantially reduced functional capacity to undertake one or more of the
following activities:
(i) communication;
(ii) social interaction;
(iii) learning
(iv) mobility
(v) self-care
(vi) self-management
When is this criterion considered met?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 33 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 33 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the permanent impairment, or
permanent impairments combined, results in substantially reduced functional capacity in one
or more of the following activities:
• Communication: how they speak, write or use sign language and gestures.
• Social interaction: how they make and keep friends, interact with the community, and cope
with feelings and emotions in social situations.
• Learning
: how they learn, understand and remember new things, and practise and use new
skills.
• Mobility: how they move around home and the community and how they get in and out of
bed or a chair.
• Self-care: how they partake in personal care, hygiene, grooming, eating and drinking, and
health.
• Self-management (if older than 6): how they organise their life, make decision, solve
problems and manage money.
•
Note: When a participant has been diagnosed with a List A condition, they will meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant is unable to participate effectively or
completely (i.e., across the whole or majority of tasks) in one or more activities, without
formally prescribed equipment?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant is unable to participant effectively or
completely in one or more activities, and usually requires the assistance of another
person?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant would be unsafe to complete one or
more tasks required to participate in an activity without formally prescribed equipment or
assistance from another person?
• Does the evidence indicate that the participant is able to participate in each activity
effectively by using commonly used items?
• Does the evidence indicate that the participant is able to participate in each activity
effectively, albeit more slowly or in a different way?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 34 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 34 of 52
link to page 35 link to page 35 link to page 35 link to page 35 link to page 26

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• Would completing tasks more slowly or in a modified way, or using commonly used items,
relieve the participant’s need for personal assistance?
In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• What specific tasks the participant cannot complete without support?
• Why the participant requires support?
• How often the participant requires support, and what that support looks like?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Does your impairment substantially reduce
your functional capacity?
For participants under the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.4 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(c)
Section 24(1)(d)?
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 24(1)(c)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
For participants over the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.4 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(c)
Section 24(1)(d)?
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 10.4 0-25 Hearing Impairments
Section 24(1)(c)
11.4 Does the participant meet Section 24(1)(d)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 35 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 35 of 52
link to page 36 link to page 36 link to page 38 link to page 38 link to page 36 link to page 36

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(d) The impairment or impairments affect the person’s capacity for social or economic
participation.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the permanent impairment, or
permanent impairments combined, affects the participant’s social or economic participation.
•
Note: Where a participant has been diagnosed with a List A condition, they will meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant’s social participation (e.g., their
capacity to play sport, go to the movies, see friends, etc.) is affected by their permanent
impairment/s - in any way?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant’s economic participation (e.g., their
capacity to travel, to find or maintain voluntary or paid work, etc.) is affected by their
permanent impairment - in any way?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant’s social and economic participation is
not impacted in any way, and that they can fully engage without any assistance?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Does your impairment affect your social, work
or study life?
For participants under the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.5 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(d)
Section 24(1)(e)?
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability support from the NDIS.
Section 24(1)(d)
• Go to
Section 12. ER Early Intervention
Requirements
For participants over the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 11.5 - Does the participant meet
24(1)(d)
Section 24(1)(e)?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 36 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 36 of 52
link to page 26

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 10.4 0-25 Hearing Impairments
Section 24(1)(d)
11.5 Does the participant meet Section 24(1)(e)?
Legislation
Section 24 Disability requirements
(1) A person meets the disability requirements if:
(e) The person is likely to require NDIS supports under the National Disability Insurance
Scheme for the person’s lifetime.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows the participant:
• will require NDIS supports for their lifetime; or
• is likely to require NDIS supports for their lifetime.
•
Note: Where a participant has been diagnosed with a List A condition, they will meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant is likely to require disability supports
that are not clinical in nature, and that focus on their functional ability, for their lifetime?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant will likely be substantially reduced in
their functional capacity (in a relevant activity) for their lifetime, despite any interventions?
• Are there any recommendations for interventions that are likely to improve the participant’s
functional capacity, and reduce their future need for disability related supports?
• If the participant is a child or young adult, does the evidence indicate that significant
functional improvements can be expected - either as they develop, or through
interventions?
• Does the participant’s need for support relate to a health condition, and is that support
more appropriately funded by the health system?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Does your impairment affect your social, work
or study life?
For participants under the age of 7
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 37 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 37 of 52
link to page 26

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Participants that meet Section
Meet the disability requirements.
24(1)(e)
Please follow the process in either :
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 24(1)(e)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
For participants over the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Meet the disability requirements.
24(1)(e)
Please follow the process in either :
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 10.4 0-25 Hearing Impairments
Section 24(1)(e)
12 ER – Early Intervention Requirements
12.1 Does the participant meet Section 25(1)(a)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 38 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 38 of 52

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
(1) A person meets the early intervention requirements if:
(a) the person:
(i) has one or more identified intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory or
physical impairments that are, or are likely to be, permanent; or
(ii) has one or more identified impairments to which a psychosocial disability is
attributable and that are, or are likely to be, permanent
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows:
• the participant has an impairment (a loss or significant change in their body’s functions or
structure, or how they think and learn); and
• the impairment is intellectual, cognitive, neurological, sensory, or physical in nature; and
• the impairment is, or is likely to be, permanent.
•
Note: Where a participant is diagnosed with a condition on List B or List D, they meet this
criterion without further assessment.
•
What to consider
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant has completed all available and
appropriate treatment options, and that there are no recommended treatment options likely
to remedy the impairment?
• Does the evidence contain recommendations for treatments which have not been
demonstrated to have been explored?
• Does the evidence indicate that the participant requires further treatment, and that this
treatment has some prospect of success?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the participant requires ongoing treatment, but that it
is for maintenance purposes only?
• Does the evidence demonstrate that the impairment is degenerative in nature, and that
treatment will not improve the impairment?
In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• What treatments have been undertaken and what were the outcomes?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 39 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 39 of 52
link to page 40 link to page 40 link to page 30 link to page 40 link to page 40

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• If there are evidence-based treatments not undertaken, why were they considered and
deemed not suitable?
• What further/ongoing treatments have been recommended and what are the expected
outcomes of these treatments?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - Do you need early intervention?
For participants under the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 12.2 - Does the participant meet
25(1)(a)
Section 25(1)(b)?
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 11 ER Disability Requirements
Section 25(1)(a)
For participants over the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 12.2 - Does the participant meet
25(1)(a)
Section 25(1)(b)?
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 25(1)(a)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
12.2 Does the participant meet Section 25(1)(b)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(2) A person meets the early intervention requirements if:
(b) the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is
likely to benefit the person by reducing the person’s future needs for supports in
relation to disability
When is this criterion considered met?
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 40 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 40 of 52
link to page 41 link to page 41 link to page 30

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows that early intervention
supports for the participant’s permanent impairment/s will reduce their need for disability-
related supports in the future.
•
Note: Where a participant has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and indicate
that this intervention will mean the participant needs less disability supports in the future?
• Does the evidence note which specific supports the participant will no longer require should
early intervention be undertaken?
• Does the evidence indicate that early intervention is likely to result in greater independence
for the participant?
• If the participant has accessed intervention before, is the outcome noted? Did previous
intervention reduce their need for disability related supports?
• Is the recommended support of a functional nature, or capacity building in nature?
In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• How the participant’s impairment is likely to impact them over time?
• What supports the participant will require if they don’t receive intervention?
• What supports the participant currently requires, and what supports (if any) the participant
is likely to require after intervention?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - How will early intervention help you?
For participants under the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 12.3 - Does the participant meet
25(1)(b)
Section 25(c)?
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 11 ER Disability Requirements
Section 25(1)(b)
For participants over the age of 7
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 41 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 41 of 52
link to page 41 link to page 41

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 12.3 - Does the participant meet
25(1)(b)
Section 25(c)?
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 25(1)(b)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
12.3 Does the participant meet Section 25(1)(c)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(1) A person meets the early intervention requirements if:
(c) the CEO is satisfied that provision of early intervention supports for the person is
likely to benefit the person by:
(i) mitigating or alleviating the impact of the person’s impairment upon the functional
capacity of the person to undertake communication, social interaction, learning,
mobility, self‑care or self‑management; or
(ii) preventing the deterioration of such functional capacity; or
(iii) improving such functional capacity; or
(iv) strengthening the sustainability of informal supports available to the person,
including through building the capacity of the person’s carer.
When is this criterion considered met?
• This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows early intervention supports
will help the participant by:
• addressing the impact of their impairment on their ability to move around, communicate,
socialise, learning, look after themselves, or organise their life
• preventing their functional capacity from getting worse
• improving their functional capacity
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 42 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 42 of 52
link to page 43 link to page 43 link to page 30

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
• supporting their informal supports to build their skills to help the participant.
•
Note: Where a participant has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and detail how
this intervention will mitigate or alleviate the impact of the participant’s permanent
impairment on their functional capacity?
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and detail how
this intervention will prevent the participant’s functional capacity from declining?
• Does the evidence contain specific recommendations for early intervention, and detail how
this intervention will improve the participant’s functional capacity?
• Does the evidence indicate that intervention is likely to strengthen the sustainability of
informal supports available to the person, and result in a decreased need for formal
disability related supports?
• In answering the above questions, does the evidence contain sufficient information
addressing:
• How the participant’s impairment is likely to impact them over time?
• What supports the participant will require if they don’t receive intervention?
• What supports the participant currently requires, and what supports (if any) the participant
is likely to require after intervention?
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines - How will early intervention help you?
For participants under the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 12.4 - Does the participant meet
25(1)(c)
Section 25(1)(d)?
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 11 ER Disability Requirements
Section 25(1)(c)
For participants over the age of 7
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 43 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 43 of 52
link to page 43 link to page 43

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Participants that meet Section
Go to
Section 12.4 - Does the participant meet
25(1)(c)
Section 25(1)(d)?
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 25(1)(c)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
12.4 Does the participant meet Section 25(1)(d)?
Legislation
Section 25 Early intervention requirements
(d) … any early intervention supports that would be likely to benefit the person as
mentioned in paragraphs (b) and (c) would be NDIS supports for the person.
When is this criterion considered met?
This criterion is considered met if evidence on the record shows early intervention supports
required are NDIS supports.
•
Note: Where a participant has been diagnosed with a condition on List D, they meet this
criterion without further assessment.
What to consider
Whether or not funding is available through other general systems is not the test of whether it
is most appropriately funded or provided through the NDIS. For example, the fact that the
health system does not adequately fund what is essentially clinical treatment (or some other
form of support that is more appropriately funded through the health system) does not make it
the responsibility of the NDIS.
For further information, refer to Our Guidelines – Is your early intervention most appropriately
funded by the NDIS?
For participants under the age of 7
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 44 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 44 of 52
link to page 30

FOI 24/25-1568
Practice Guide
For Internal Use Only
OFFICIAL
Participants that meet Section
Meet the early intervention requirements.
25(1)(d)
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Participants that do not meet
Go to
Section 11 ER Disability Requirements
Section 25(1)(d)
For participants over the age of 7
Participants that meet Section
Meet the early intervention requirements.
25(1)(d)
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
Participants that do not meet
Are not eligible for disability or early intervention
Section 25(1)(d)
support from the NDIS.
Please follow the process in either:
• knowledge article KA – Complete an Eligibility
Check
• knowledge article KA – Finalise an Eligibility
Reassessment decision
13 Related procedures or resources
• National Disability Insurance Scheme (Becoming a Participant) Rules 2016
• NDIS Amendment Act 2024
• Our Guidelines - Applying to the NDIS
3.4 2024-09-19 Access and ER Decision Tree Practice Guide
Page 45 of 46
This document is uncontrolled when printed
OFFICIAL
Page 45 of 52
link to page 47 link to page 47
FOI 24/25-1568
DOCUMENT 2
OFFICIAL
For Internal Use Only
Description of Impairment Categories
1.
Intellectual – such as how you speak and listen, read and write, solve problems,
and process and remember information.
An intellectual impairment may be considered a developmental disorder as it becomes
apparent at an early ag
e1. Without these skills, a person needs additional supports to
succeed at school, work, or independent life. Conditions such as Down’s syndrome and
cerebral palsy may be associated with intellectual impairments.
2.
Cognitive – such as how you think, learn new things, use judgment to make
decisions, and pay attention.
Cognitive impairment involves various aspects of high-level mental functions and
processes such as attention, memory, knowledge, decision-making, planning,
reasoning, judgment, perception, comprehension, language, and visuospatial functio
n2.
There are some similarities with intellectual impairments however, cognitive
impairments generally become apparent at a later stage in life and are associated with
brain injury or pathology1. Conditions such as dementia and traumatic brain injury may
cause cognitive impairments.
3.
Neurological – such as how your body functions
.
Neurological Impairments occurs when there is a change in function of the nervous
system, which includes the brain and spinal cord2. Damage to either or both areas can
affect the way the nervous system processes information. Parkinsons disease, epilepsy
and multiple sclerosis3 are conditions which have a neurological basis.
4.
Sensory – such as how you see or hear
Sensory impairment most commonly relates to hearing or visual loss but can include all
senses2.
5.
Physical – such as the ability to move parts of your body
Physical impairment may cause limitations in posture control, moving and coordinating
parts of the body or in stamina2. There are many conditions which can cause a physical
impairment including amputation of a limb, arthritis, multiple sclerosis, heart disease.
6.
Psychosocial -
This means you have reduced capacity to do daily life activities and
tasks due to your mental health.
Participants with a psychosocial impairment may find it hard to engage in education,
training and employment or engage with the community. Mental health conditions such
as bipolar affective disorder and schizophrenia are commonly associated with
psychosocial impairments1 but other conditions such as autism could also have
associated psychosocial impairments.
1 The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.; DSM–5; American Psychiatric Association, 2013)
2 International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health: ICF. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2001.
3 World Health Organization(WHO). (1993).
The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders. World Health
Organization.
OFFICIAL
Page 47 of 52
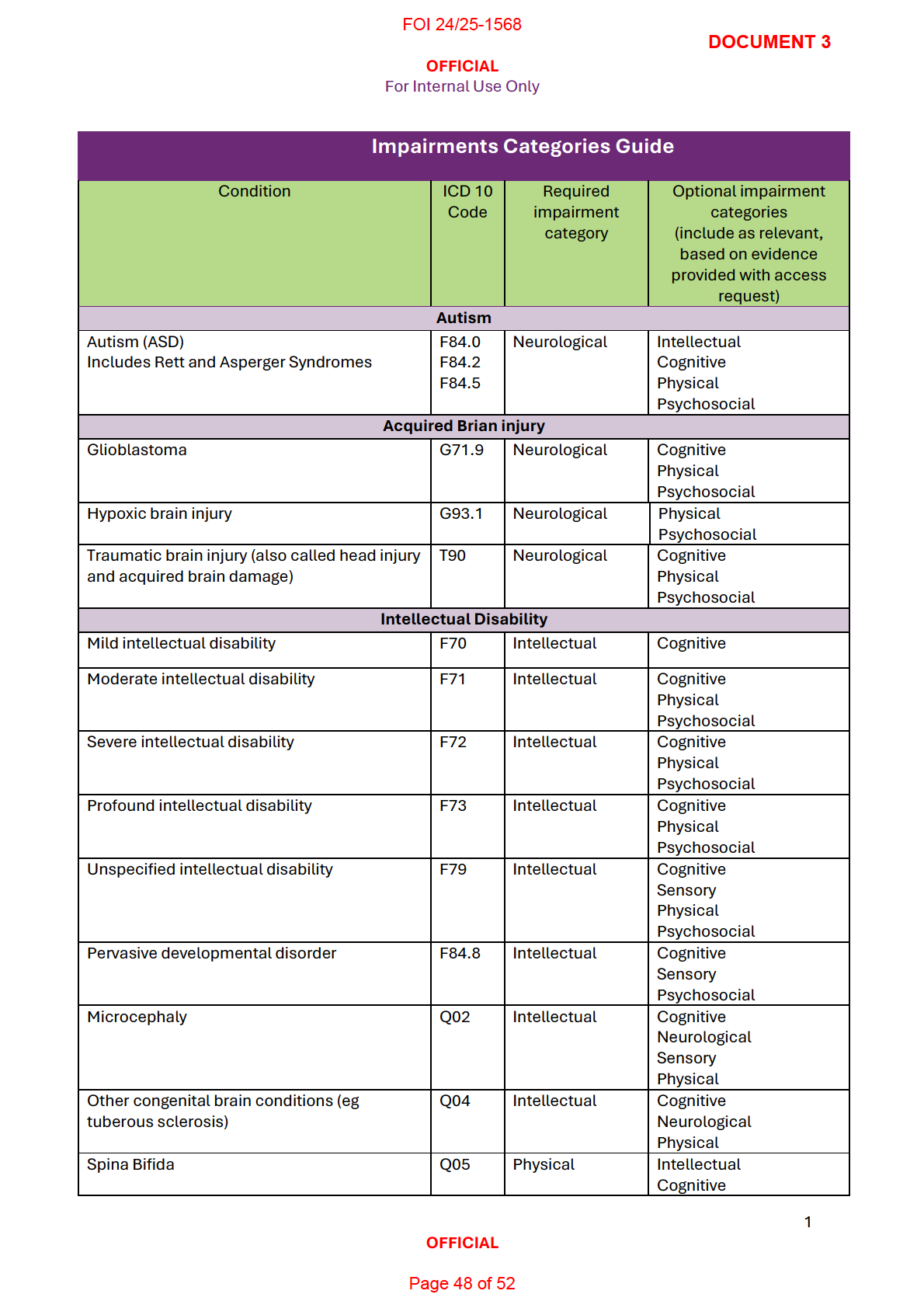
FOI 24/25-1568
OFFICIAL
For Internal Use Only
Sensory
Neurological
Foetal alcohol syndrome
Q86.0
Neurological
Intellectual
Foetal alcohol spectrum disorder (Q86.0D)
Q86.0D
Cognitive
Sensory
Physical
Psychosocial
Cornelia de Lange syndrome
Q87.1
Intellectual
Cognitive
Neurological
Sensory
Physical
Psychosocial
Prader Willi syndrome
Q87.1
Intellectual
Cognitive
Neurological
Physical
Psychosocial
Coffin-Lowry syndrome
Q87.8
Intellectual
Cognitive
Neurological
Sensory
Physical
Psychosocial
Other congenital conditions (causing
Q89
Intellectual
Cognitive
intellectual disability)
Neurological
Sensory
Physical
Psychosocial
Edwards syndrome
Q91
Intellectual
Cognitive
Neurological
Sensory
Physical
Psychosocial
Patau syndrome
Q91
Intellectual
Cognitive
Neurological
Sensory
Physical
Psychosocial
Cri du Chat syndrome
Q93.4
Intellectual
Cognitive
Sensory
Physical
Angelman syndrome
Q93.5
Intellectual
Cognitive
Neurological
Physical
Other chromosomal syndromes (including
Q99
Intellectual
Cognitive
Kabuki & Williams syndromes)
Neurological
Sensory
Physical
Psychosocial
Fragile X syndrome
Q99.2
Intellectual
Cognitive
Neurological
Sensory
Physical
2
OFFICIAL
Page 49 of 52